Corporate finance is a critical aspect of business operations that focuses on managing a company’s financial resources. This discipline encompasses various activities aimed at maximizing shareholder value while managing financial risks. Understanding corporate finance is essential for business leaders, investors, and stakeholders who want to navigate the financial landscape effectively.
Definition of Corporate Finance
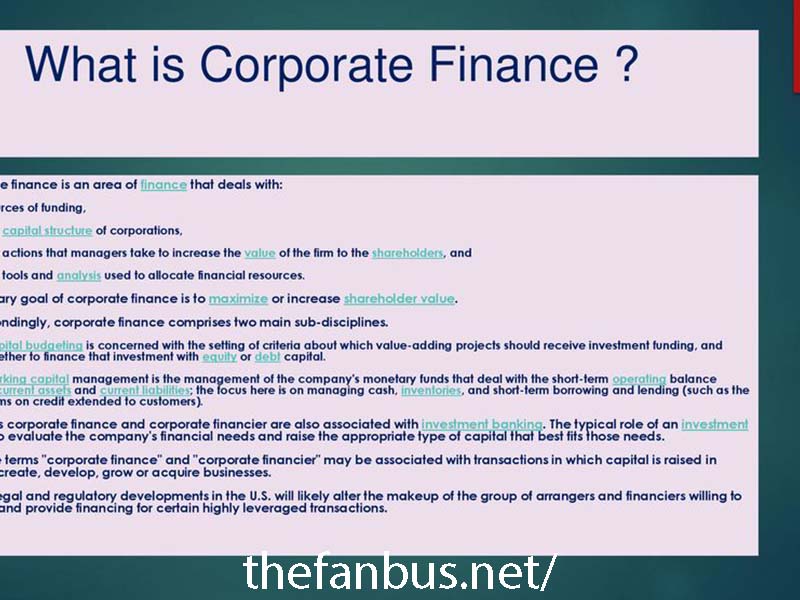
At its core, corporate finance deals with the planning, raising, and managing of funds for businesses. It involves strategic financial decision-making to ensure that the organization can meet its goals and obligations. The primary functions of corporate finance include capital budgeting, capital structure, and working capital management.
Capital Budgeting
This involves evaluating potential investment opportunities to determine their feasibility and alignment with the company’s strategic objectives. Decisions about which projects to fund are crucial, as they can significantly impact the company’s future growth and profitability.
Capital Structure
This refers to the mix of debt and equity financing used to fund the company’s operations and growth. A balanced capital structure is vital, as it influences the company’s risk profile and overall cost of capital.
Working Capital Management
This focuses on managing the company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure sufficient liquidity for daily operations. Effective working capital management helps prevent cash flow issues that could jeopardize the company’s financial health.
Importance of Corporate Finance
Understanding corporate finance is essential for several reasons
Value Creation
Corporate finance plays a crucial role in creating value for shareholders. By making informed financial decisions, companies can increase their market value and provide a good return on investment.
Risk Management
Effective corporate finance practices help organizations identify, assess, and manage financial risks. This proactive approach enables companies to navigate uncertainties in the market and maintain stability.
Strategic Planning
Corporate finance is integral to a company’s strategic planning process. Financial analysis and forecasting help organizations set realistic goals, allocate resources efficiently, and measure performance.
Investor Confidence
A solid understanding of corporate finance enhances transparency and builds trust among investors. When companies demonstrate sound financial management, they are more likely to attract investment and support from stakeholders.
Key Concepts in Corporate Finance
Time Value of Money
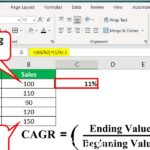
One of the fundamental principles of corporate finance is the time value of money (TVM). This concept states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future due to its potential earning capacity. TVM is crucial in capital budgeting decisions, as it helps assess the profitability of investments over time.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
DCF analysis is a valuation method used to estimate the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows. By discounting these cash flows back to their present value using a discount rate, businesses can determine whether an investment is worthwhile. This technique is widely used in corporate finance to evaluate projects, mergers, and acquisitions.
Cost of Capital
The cost of capital represents the minimum return that a company must earn on its investments to satisfy its investors. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating investment opportunities and is essential in determining the appropriate capital structure. A lower cost of capital typically indicates a lower risk profile, which can make it easier for a company to raise funds.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are essential tools for analyzing a company’s performance and financial health. Common ratios include the debt-to-equity ratio, return on equity (ROE), and current ratio. These metrics provide insights into a company’s profitability, liquidity, and leverage, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
Corporate Finance Functions
Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)
FP&A is a critical function within corporate finance that involves budgeting, forecasting, and performance analysis. This process helps organizations plan their financial future and make data-driven decisions. By assessing historical data and market trends, FP&A teams can provide valuable insights that guide strategic planning.
Treasury Management
Treasury management is responsible for managing a company’s cash flow, liquidity, and financial risks. This function ensures that the organization has sufficient funds to meet its operational needs while optimizing its investment portfolio. Effective treasury management helps companies mitigate risks related to currency fluctuations and interest rates.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Corporate finance plays a crucial role in facilitating mergers and acquisitions. Financial professionals evaluate potential targets, conduct due diligence, and structure deals to maximize value for the acquiring company. M&A activity can significantly impact a company’s growth trajectory and market position.
Investor Relations
Investor relations (IR) is the communication link between a company and its shareholders. Corporate finance professionals play a key role in developing IR strategies, presenting financial performance, and addressing shareholder concerns. Maintaining strong investor relations is vital for building trust and securing ongoing investment.
Challenges in Corporate Finance
Despite its importance, corporate finance faces several challenges
Economic Uncertainty
Economic fluctuations and uncertainties can significantly impact financial markets and corporate performance. Companies must navigate changing interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical risks that can affect their capital structure and investment decisions.
Regulatory Compliance
Corporate finance professionals must adhere to various regulations and reporting standards. Compliance with these requirements is essential for maintaining transparency and avoiding legal repercussions. Staying updated on changes in regulations is crucial for effective financial management.
Technological Disruption
The rapid advancement of technology has transformed the corporate finance landscape. Automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are reshaping financial processes, requiring professionals to adapt and embrace new tools. Staying competitive in this evolving environment is essential for corporate finance teams.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors
Increasingly, stakeholders are considering ESG factors in their investment decisions. Corporate finance professionals must incorporate these considerations into their financial strategies to align with evolving market expectations. Addressing sustainability and ethical concerns is becoming an integral part of corporate finance.
Conclusion
Corporate finance is a vital discipline that influences the financial health and growth of businesses. By understanding its key concepts and functions, organizations can make informed decisions that maximize shareholder value while managing risks. Despite the challenges faced in this field, effective corporate finance practices are essential for navigating the complexities of the modern business environment. As companies continue to adapt to changing market dynamics, a solid grasp of corporate finance will remain crucial for success.
By prioritizing financial planning, risk management, and strategic decision-making, businesses can enhance their financial performance and secure a prosperous future. In an era of economic uncertainty and technological disruption, corporate finance professionals play a pivotal role in guiding organizations toward sustainable growth and value creation.